
There are two configuration modes available in the alternatives system, manual and automatic mode. For this post, we will download the tarball, the ‘jdk-7u45-linux-圆4.tar.gz’ file.
rpm (Red Hat Package Manager) file and a. The Linux file formats available for download, are a. At the time of this post, that is JDK 7u45 (aka 1.7.0_45-b18). According to Oracle, the ‘OpenJDK is an open-source implementation of the Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE) specifications’. We will choose the latest commercial version of Oracle’s JDK. Therefore, we will download the most recent version of the 64-bit Linux JDK. We could choose either Oracle’s commercial version of Java or the OpenJDK version. In the above screen grab, you see our VM is running a 64-bit version of Ubuntu 12.04.3 LTS (Precise Pangolin). As developers, we will choose to install the JDK. The JDK includes a complete JRE, plus tools for developing, debugging, and monitoring Java applications. The Java Development Kit (JDK) purpose is to develop Java applications. The Java Runtime Environment (JRE) purpose is to run Java applications.

Executing an ‘ls -Al /usr/bin/* | grep -e java -e jar -e appletviewer -e mozilla-javaplugin.so’ command, we see that each Java executable is actually a symbolic link to the alternatives directory, not a binary executable file.įind Your Processor’s Architecture JRE or JDK? This directory contains the majority of binary executables on the system. We can see this system at work by changing to our ‘/usr/bin’ directory. Instead, it is a symbolic link to a name in the alternatives directory, which in turn is a symbolic link to the actual file referenced.’ The alternatives system and the system administrator together determine which actual file is referenced by this generic name. The generic name is not a direct symbolic link to the selected alternative.

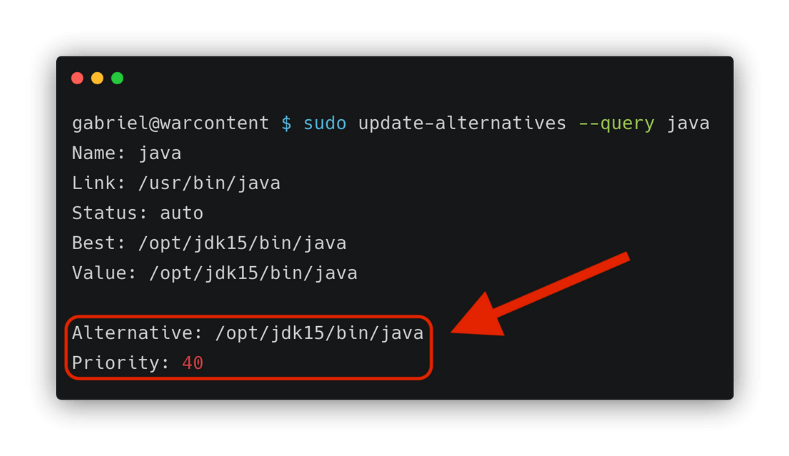
AlternativesĪccording to, alternatives ‘make it possible for several programs fulfilling the same or similar functions to be installed on a single system at the same time. A generic name in the filesystem is shared by all files providing interchangeable functionality. In a many software development environments, you may need different versions of Java, depending on different client project’s level of technology. By selecting an alternative version of Java, we control which java.exe binary executable file the system calls when the ‘java’ command is executed. These three versions are referred to as ‘alternatives’, thus the ‘alternatives’ command. There are two other Java versions also installed but not active, an Oracle 1.7.0_17 JRE version and an older 1.7.0_04 JDK version. That version is located in the ‘/usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.7.0_17’ subdirectory. In the above example, the 1.7.0_17 JDK version of Java is configured and active.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
